
As more and more sectors are becoming dependent on computer technology, the COE Department will continue to keep abreast of the latest computer technology, in order to better equip the learners with vast knowledge preparing them to be of service to the community.
The Computer Engineering Department takes it as a responsibility to educate students with the desire to improve the quality of their family lives and the people in the community. The members of the faculty work without let up, as they believe that giving quality education is a noble way to make a difference in society.
Please take time to explore our page and discover what we do best.
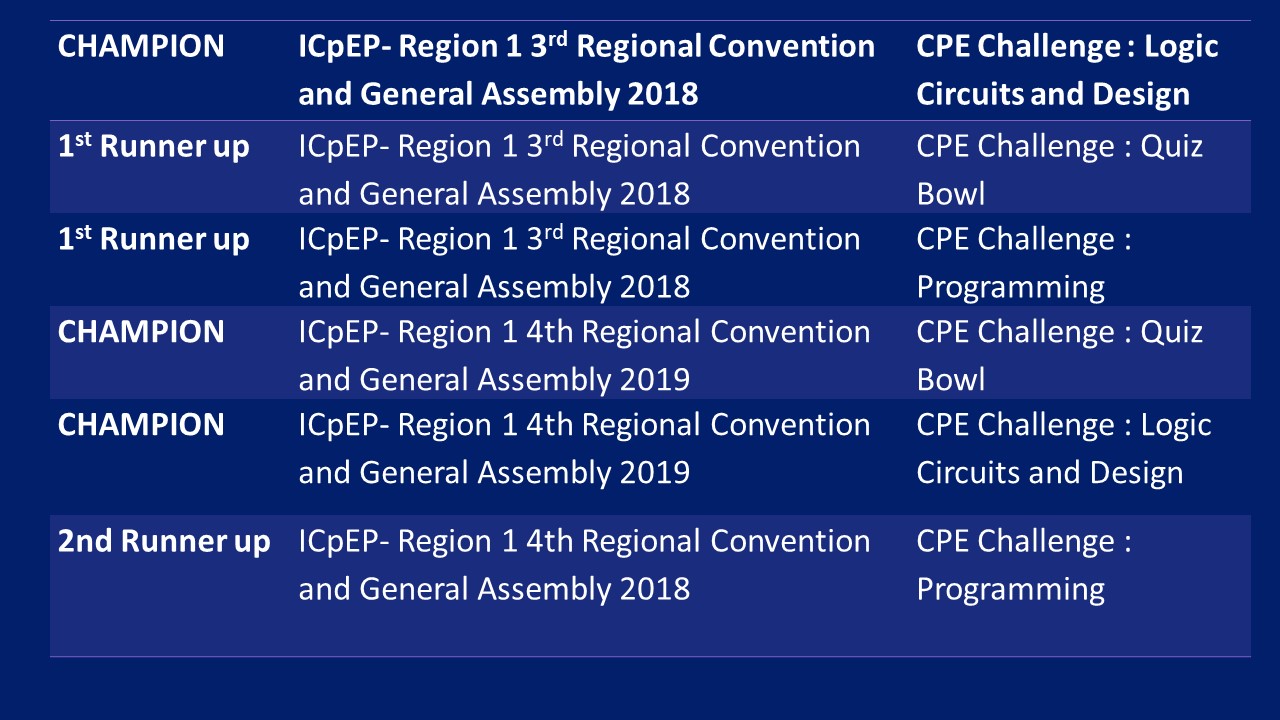
Accreditation Status: AACCUP LEVEL II Re-accredited

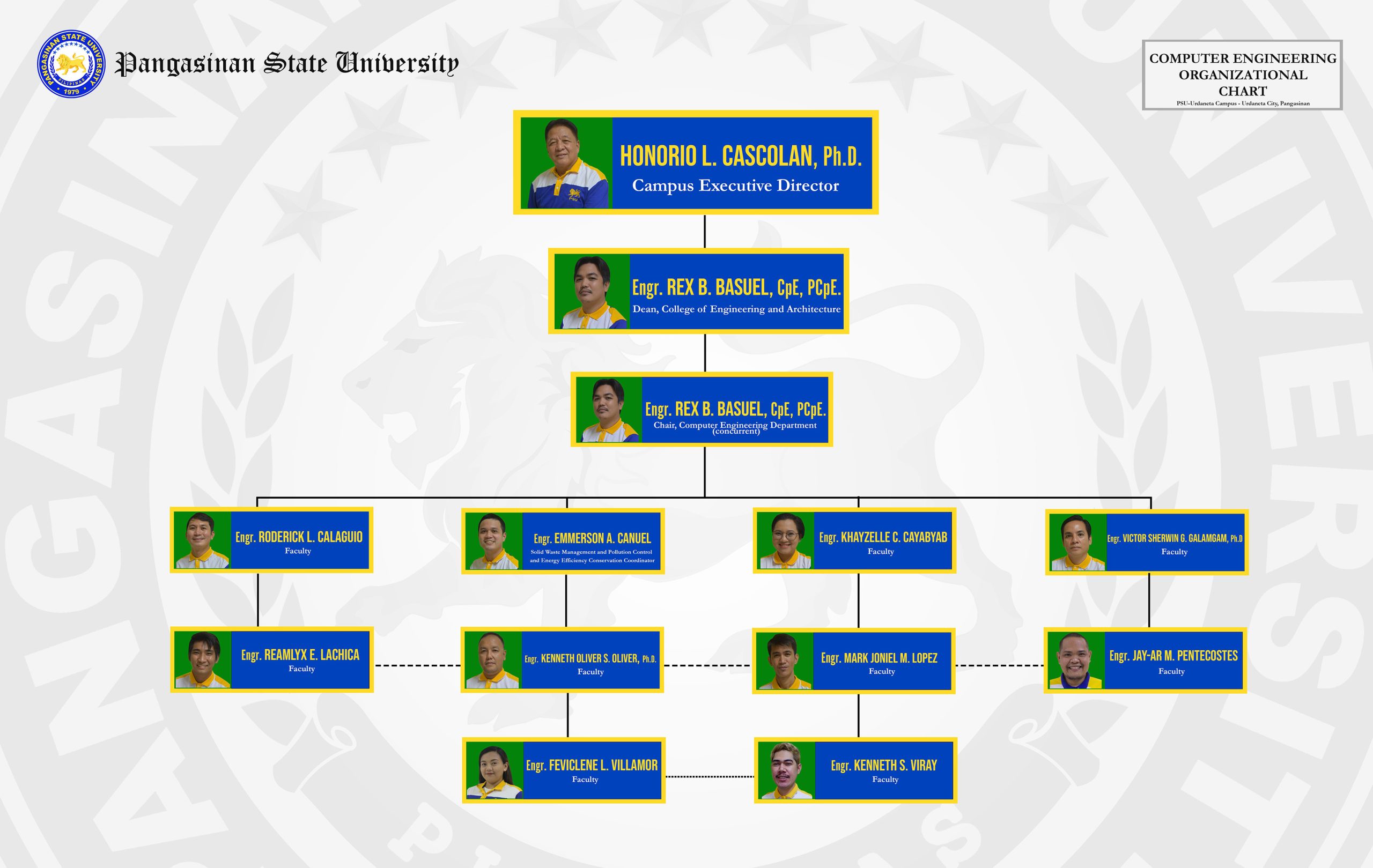
Organizational Chart
EMPLOYMENT OPPORTUNITIES
- Hardware Systems Designer
- Smart Phone Designer
- Robotics Specialist
- Information Security Administrator
- Multimedia Technologist
- Network Administrator
- Network Engineer
- Systems Analyst
- Software Engineer
- Systems Engineer
- Software Security Engineer
- Telecommunications Engineer
Three (3) to five (5) years after graduation, graduates of the Bachelor of Science in Computer Engineering program should;
- be globally competitive in the field of Computer Engineering;
- be equipped with necessary and relevant technical competencies that are contributory to national development.
- be able to demonstrate managerial and leadership roles in their organizations and multi-sectoral communities.
- be able to exhibit high levels of professionalism and ethical responsibility and work collaboratively.
- be a lifelong learner that are imbued with the Pangasinan State University core values
|
|
GRADUATE ATTRIBUTES |
INSTITUTIONAL LEARNING OUTCOMES |
PROGRAM OUTCOMES |
PERFORMANCE INDICATOR |
|
|
|
1. Engineering Knowledge |
ILO3, ILO4 |
a. Solve complex engineering problems: by applying mathematics and Sciences. |
· Apply knowledge of required mathematics (e.g., Differential Equations, statistics, probability, discrete mathematics, etc.) in resolving computer engineering problems. · Apply knowledge of science (e.g., conductors, insulators, mechanics, semiconductor physics, Computer Science, Chemistry) in studying computer engineering problems. · Apply knowledge of engineering (e.g., electronics, control systems, VLSI, communications and networks, software systems, computer architecture, embedded systems) in the development of systems related to computer engineering. |
|
||
|
2. Investigation |
ILO2, ILO5, ILO13 |
b. Design and conduct experiment as well as analyze and interpret data |
· Identify the constraints, assumptions, and models for the experiment and use appropriate equipment and techniques for data collection. |
|
||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
· Analyze discrepancies in experimental results and determine whether the error is within acceptable experimental limits. · Validate experimental results with respect to assumptions, constraints, and theory. |
|
|
3. Design/ development of solutions |
ILO1, ILO2, ILO5 |
c. Design a system, component, or process to meet desired needs within realistic constraints such as economic, environmental, social, political, ethical, health and safety, manufacturability, and sustainability, in accordance with standards; |
· Design mechatronics, robotics, and computer network systems using multiple appropriate constraints. · Apply Code and Standards in the design of the system. · Measure the impact of developed Computer Engineering system using quantitative measurement ( performance measures, indicators, etc.) in end• users’ everyday lives. |
|
||
|
4. Individual and Teamwork |
ILO2, ILO5, ILO10 |
d. Functions on multidisciplinary teams. |
· Developed responsibilities, reliability and maintain a high level of professionalism in a multidisciplinary setting. · Produce a variety of documents using appropriate formats and grammar with discipline-specific conventions, including citations. · Delivers well-organized, logical oral presentations, including good explanations when questioned. |
|
||
|
5. Problem Analysis |
ILO3, ILO4 |
e. Identify, formulate and solve complex engineering problems. |
· Analyze key points and compute engineering problems. · Apply concepts of mathematics to solve engineering and technology Problems. · Formulate an appropriate approach to solve engineering and technology · Problems. |
|
||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
6. Ethics Understanding and Level of Practice |
ILO1, ILO6, ILO11 |
f. Practice professional and ethical responsibility |
· Apply professional responsibility (e.g., safety, environmental, legal, regulatory, intellectual property, project management, risk management). · Apply ethical responsibility (e.g., Code of Ethics defined by PSU Ethics Board, IEEE, and Institute of Computer Engineers of the Philippines) · Preserves the ethics and integrity of the CpE profession. |
|
|
7. Communication |
ILO1, ILO3, ILO4, ILO9 |
g. Communicate effectively with a varied audience. |
· Demonstrates an excellent understanding of the context of the thesis/research/project/report topic and existing methods. · Produce effective written documents, including lab reports, term papers, and a research manuscript. · Deliver an effective research/thesis/project presentation. |
|
||
|
8. Environment and Sustainability |
ILO5, ILO2 |
h. Innovative education is necessary to understand the impact of engineering solutions in a global, economic, environmental, and social context. |
· Evaluate and describe accurately the environmental impact of computer engineering products, including those course and thesis projects; · Evaluate and describe accurately environmental and economic tradeoffs in computer engineering products, including those including those course and thesis projects; · Evaluate and describe accurately the health/safety and economic tradeoffs in computer engineering products, including those course and thesis projects; |
|
||
|
9. Lifelong Learning |
ILO2, ILO3 |
i. Engage in lifelong learning and keep abreast with the developments in computer Engineering. |
· Participate in the conduct of field works and experiments related to the field of computer engineering. |
|
||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
· Dynamically participate in the conduct of continuing professional development programs of the university and the industry. · Recommend a strategic method to career/professional development planning. |
|
|
10. The Engineer and Society |
ILO3, ILO5, ILO7 |
j. Knowledge of contemporary issues. |
· Identify the role of Computer Engineering on the current social, economic, political, environmental, and industrial issues. · Identify the importance of engineering and technology on the current social, economic, political, environmental, and industrial issues. · Implements the effects of the current local, national, and international issues in the engineering and technology practice. |
|
||
|
11. Modern Tool Usage |
ILO4 |
k. Use techniques, skills, and modern engineering tools necessary for engineering practice. |
· Demonstrate the functionality, operation, and application of modern engineering tools. · Effectively utilize computer programming software, instrumentation equipment, and measurement techniques for the building, testing, and operating of electronic circuits and systems. · Demonstrate knowledge of digital electronics theory and microcomputer architecture. |
|
||
|
12. Culturally Responsive |
ILO2, ILO4, ILO5 |
l. Act as a team leader and member of computer engineering projects by employing their management principles in a multidisciplinary environment. |
· Understand managerial concepts and techniques used in the real world by Technical Managers, Project Directors, and other technically oriented management personnel. · Develop a sense of responsibility & leadership in a multidisciplinary setting. · Apply knowledge and understanding in managing human resources in a multidisciplinary environment. |
|
||
- Institute of Computer Engineers of the Philippines (ICpEP)
- Mechatronics and Robotics Society of the Philippines (MRSP)










